Welcome to the Synth Tutorial series! If you're new to the world of synthesizers or just getting started with our SkyDust 3D, you're in the right place. In this series, we'll walk you through the fundamentals of sound synthesis using our SkyDust 3D. This article is dedicated to getting Envelope Generators explained. Don't forget to stop by the first article about Oscillators.
In our previous session, we discussed oscillators and their role in shaping sound. Today, we will delve into another essential component of synthesizers: Envelope Generators.
What are Envelope Generators?
Envelope Generators (EGs) are responsible for generating the envelope of a sound. They determine how the sound evolves over time, whether it starts abruptly, gradually fades in and out, or sustains at a certain level. By manipulating its parameters, you can control the attack, decay, sustain, and release stages of a sound, molding it to your creative vision. In SkyDust, you can control the gain of each oscillator through each dedicated EG per oscillator.
Parameters of Envelope Generators
Envelope Generators can have up to six parameters:
- Delay: The delay setting allows you to introduce a time gap before a particular oscillator starts playing. This feature can be useful when creating layered sounds or intricate arrangements.
- Attack Time: This determines the duration it takes for the sound to reach its peak volume. A fast attack creates an immediate rise, while a slower attack builds up the sound gradually.
- Hold: The hold parameter acts as an initial sustain, maintaining a constant level before the decay stage begins. This can add a sustained layer to the sound, enhancing its complexity and texture.
- Decay Time: The decay time sets the duration for the sound to diminish from its peak volume to the sustain level. A shorter decay time results in a quicker decay, while a longer decay time allows for a more gradual decrease.
- Sustain Level: This parameter defines the volume level at which the sound will sustain after the decay stage. Higher sustain levels maintain the sound at a louder volume, while lower levels create a softer sustained sound.
- Release Time: When the note is released, the release time determines how long it takes for the sound to fade out completely. A shorter release time results in a quick fade-out, while a longer release time adds a gradual fade.
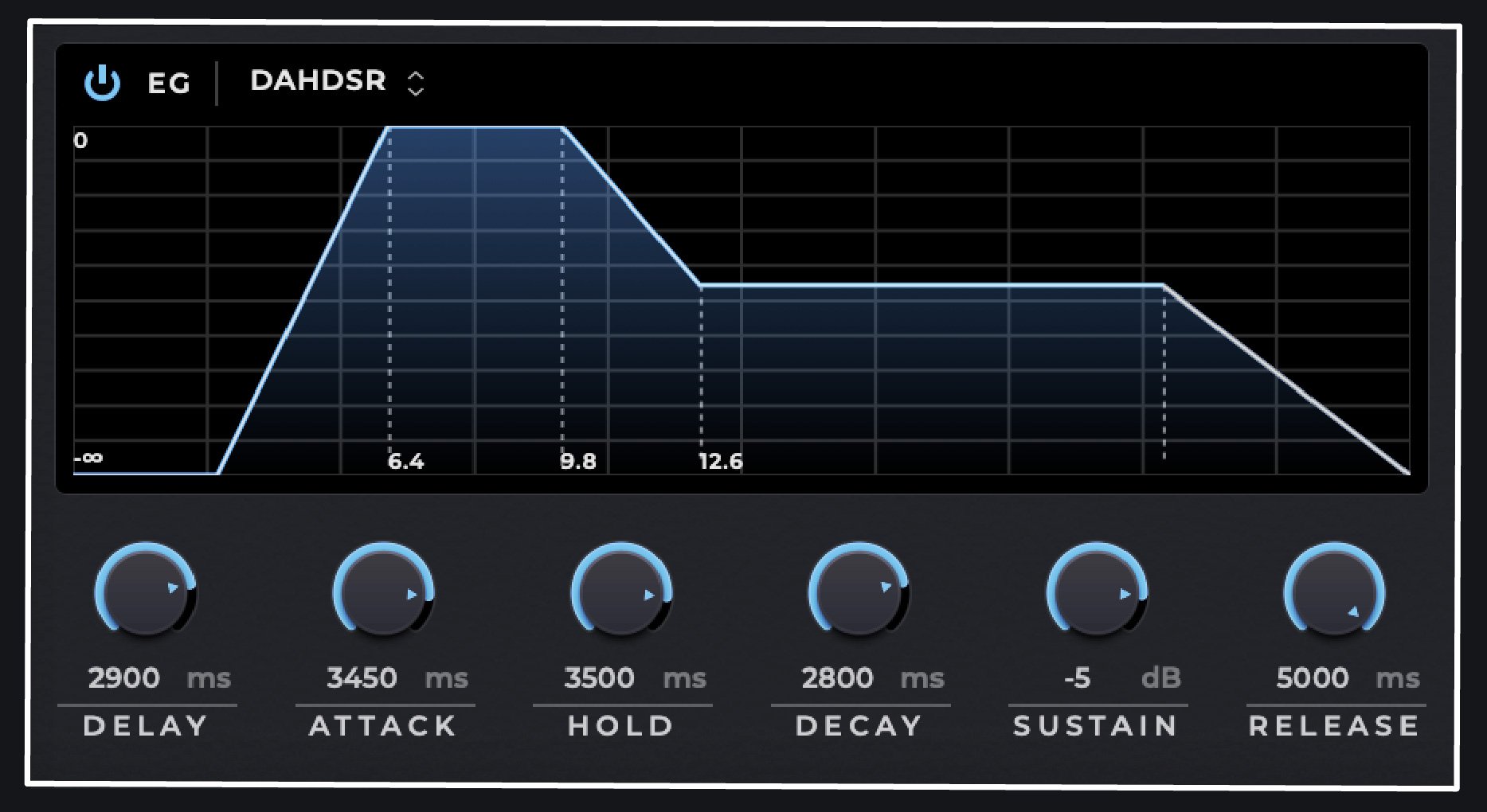
Models of Envelope Generators
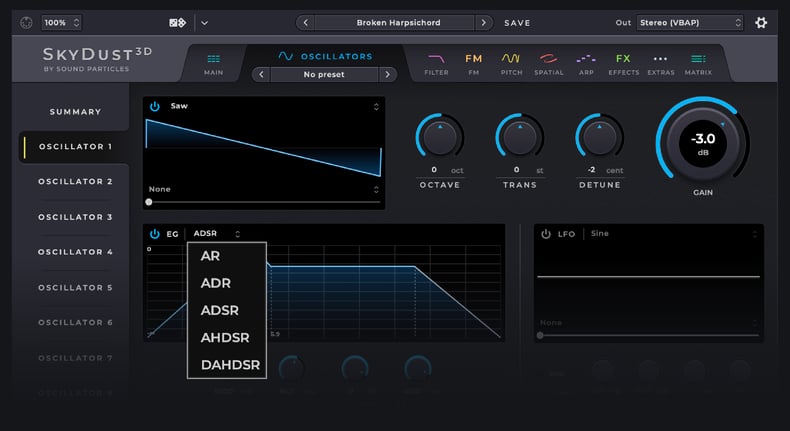
There are different models of EGs. Here are a few types you may come across:
- ADSR: The ADSR (Attack, Decay, Sustain, Release) envelope is the most widely used type. It allows for precise control over the attack time, decay time, sustain level, and release time of the sound.
- AR: The AR (Attack, Release) envelope is often used for percussive sounds or short bursts of sound. It starts with an attack stage, quickly reaches its peak level, and then enters the release stage as soon as the note is released.
- ADR: The ADR (Attack, Decay, Release) is a simplified version of the ADSR model, omitting the Sustain stage. It is suitable for shaping percussive or transient sounds rather than sustained sounds.
- AHDSR: The AHDSR (Attack, Hold, Decay, Sustain, Release) allows for more precise control over the shape and duration of the sound envelope. It is suitable for a wide range of sounds, from short percussive hits to long sustained sounds with complex decay and release characteristics.
- DAHDSR: The DAHDSR (Delay, Attack, Hold, Decay, Sustain, Release) provides more precise control over the envelope shaping process. It enables the creation of intricate and nuanced sounds with delayed attacks, sustained levels, and unique rhythmic patterns, adding depth and complexity to synthesized sounds.
It's important to note that not all synthesizers or software instruments may include all of these envelope types. The availability and functionality of Envelope Generators can vary depending on the specific synthesizer or software you are using. In SkyDust you can find all the mentioned above.
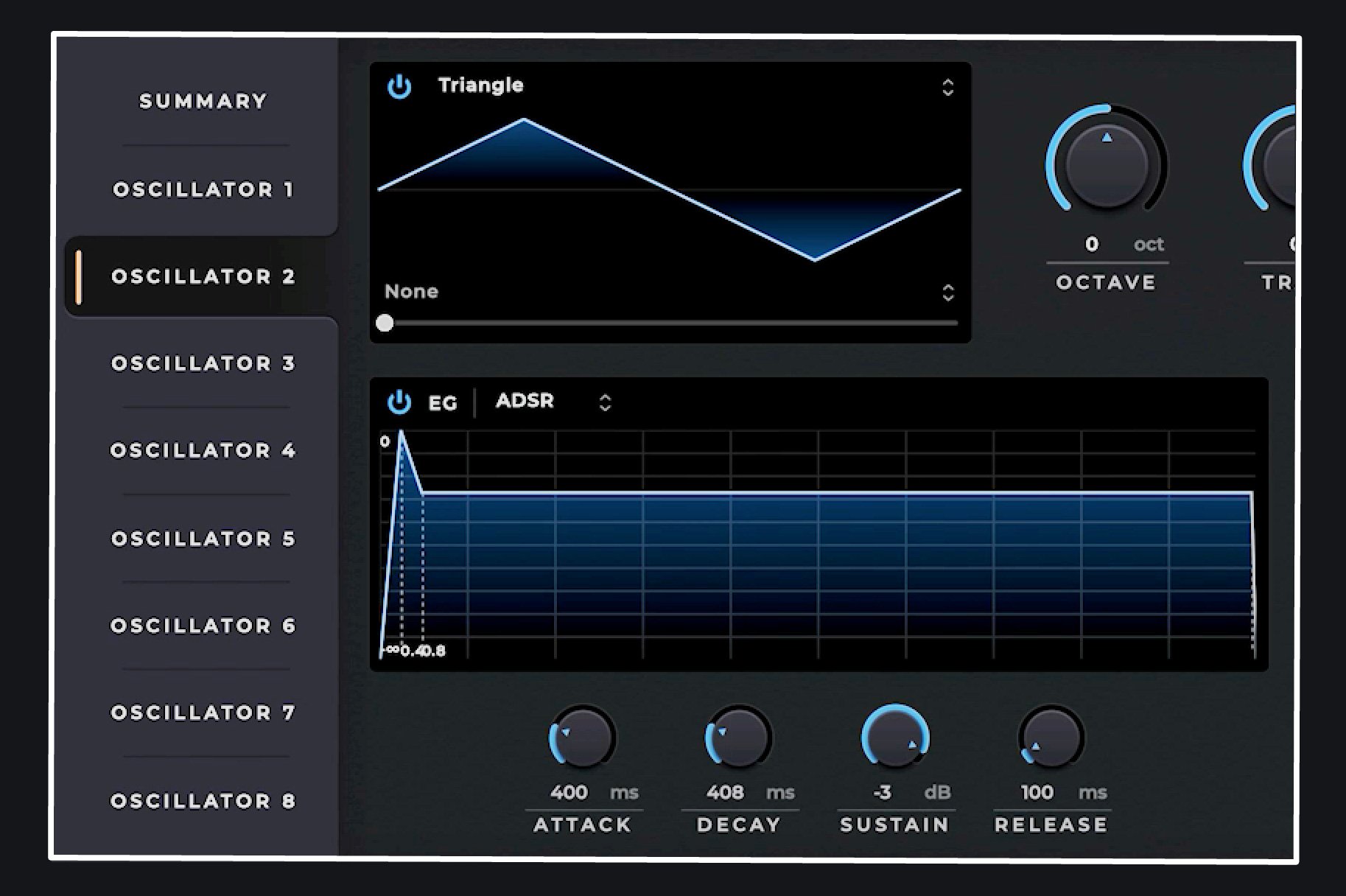
Exploring Timbre Control with Multiple Oscillators
One fascinating aspect of Envelope Generators is their impact on timbre. When multiple oscillators with different envelope settings interact, they create complex and evolving tonal characters, offering endless possibilities for sound design and achieving unique and evolving timbres.
For example, by using a square wave with a fast attack and decay, followed by a sustaining triangle wave, we can create a sound that starts with a bright, punchy attack and transitions to a mellow sustain. This combination of envelope settings modifies the timbre throughout the sound's duration.
Mastering EGs
Envelope Generators are powerful tools in sound design, allowing you to shape the dynamics and timbre of your synthesized sounds. To become an envelope maestro, understanding the ADSR model and how to adjust the attack, decay, sustain, and release parameters, is the first step and it opens up a world of creative possibilities. Additionally, utilizing envelope generators with different settings for each oscillator enables you to craft complex and evolving timbres, creating captivating sounds that will delight your listeners.
Once you've mastered EGs and Oscillators, move forward to the next tutorial to learn additional components of a synthesizer and start exploring modulation possibilities to start bringing life and movement to your sounds.
See you on the next tutorial!
Stay tuned and join the revolution!
Topics: Sound Particles, Sound Design, Tutorials, 3D audio, Surround Sound, Music, synth, virtual instrument, synthesizer, SkyDust3D

